Antimicrobial Resistance
Our future depends on what we do today.

- About
- Prevention
- Antibiotic Stewardship
- Surveillance
- Awareness
- Resources
Since the introduction of penicillin in 1942, antimicrobials have transformed the treatment of infections and saved millions of lives. But organisms “resistant” to penicillin were noticed from almost the very beginning. Now, decades of misuse and outdated guidelines have driven a rise in the organisms that are resistant to these lifesaving drugs.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of miroorganisms (including bacteria, fungi, viruses, etc.) to nullify the effects of antimicrobial drugs, resulting in these drugs becoming ineffective.1,2 AMR can affect anyone, of any age, in any country. 1
Today, AMR is one of the world’s greatest health threats, causing over 1 million deaths each year, and that number is growing.3
The severity has prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) to declare AMR as one of the top 10 global public health threats facing humanity.4
As the problem continues, common medical procedures will become increasingly life-threatening. Left unabated, the problem will grow exponentially, literally threatening every person on earth.
AMR occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines designed to kill them.
As a result of drug resistance, infections become harder to treat, increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.

1. High number of bacteria
Whenever there is a high number of bacteria, a small number of them are resistant to antibiotics.

2. Antibiotics kill bacteria
When taken, antibiotics kill bacteria causing the illness but they also kill the good bacteria that protect the body from infection.

3. Resistant bacteria grow and multiply
The resistant bacteria can now grow and multiply without competition.
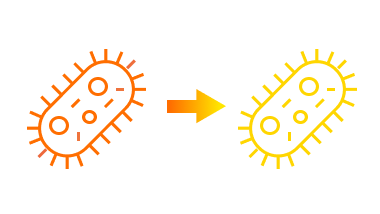
4. Transfer of resistance
Some bacteria can transfer their resistance to antibiotics to other bacteria, which can cause more problems.

If left unabated, the effects of AMR could be worse than COVID-19. 6,11 Future projections suggest that AMR could result in millions of deaths and trillions of dollars in lost global production. 7
As the problem continues, common medical procedures will become increasingly life-threatening. The problem can grow exponentially, literally threatening every person on earth.
The Global Fight Against Antimicrobial Resistance
From Broadview Pictures @2022. Silent Pandemic was produced by Broadview Pictures in co-production with ZDF and in cooperation with ARTE. All rights reserved. Used under agreement.
Our global public health efforts seek to expand access and drive capacity-building through partnerships with leading organizations and governments.
We engage in advocacy with governments, funders and health agencies to advance innovations to address the world’s leading public health needs, including drug-resistant infections.
We possess important capabilities that are instrumental in containing AMR. We offer a wide range of medical products, platforms and offerings that can be used to prevent the spread of infection in healthcare facilities, such as diagnostic systems to screen, test and diagnose infection, including drug-resistant strains, as well as state-of-the-art surveillance and reporting capabilities to monitor, track and predict AMR outbreaks.
Enabled by our innovative programs and technologies, BD teams across the globe are directly engaging AMR leaders in government, academia and professional societies to strengthen AMR awareness, health systems, capacities and infection prevention and diagnostic practices.
BD is leveraging its extensive global capabilities to meaningfully engage around 5 key strategies to reduce the burden of drug-resistant infections.
We must take action against drug-resistant infections, TOGETHER!
New and Newsworthy
References
1. World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance fact sheet. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs194/en/. Accessed November 28, 2017.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About antimicrobial resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about.html. Accessed May 12, 2017.
3. Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. The latest estimates of global anti-microbial resistance showurgent policy action is needed to save lives. https://www.healthdata.org/news-release/latest-estimatesglobal-anti-microbial-resistance-show-urgentpolicyactionneededsave#:~:text=An%20estimated%204.95 %20million%20people,young%20children%20are%20particularly%20affected. Accessed February 8, 2022.
4. World Health Organization. Ten threats to global health in 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-toglobal-health-in-2019. Accessed February 8, 2022.
5. Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022;399(10325):629-655.
6. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. More people in the United States dying from antibioticresistant infections than previously estimated. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p1113-antibioticresistant. html; Accessed June 23, 2022.
7. O’Neill J. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. https://amrreview.
org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20%20Tackling%20a%20crisis%20
for%20the%20health%20and%20wealth%20of%20nations_1.pdf. Accessed February 8, 2022.
8. Smith R, Coast J. The true cost of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ. 2013;346:f1493.
9. World Bank. By 2050, drug-resistant infections could cause global economic damage on par with 2008
financial crisis, http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2016/09/18. Accessed October 12, 2017.
10. Shapiro DJ, Hicks LA, Pavia AT, Hersh AL. Antibiotic prescribing for adults in ambulatory care in the USA,
2007–09. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;69(1):234-240.
11. Ukuhor H. The interrelationships between antimicrobial resistance, COVID-19, past, and future
pandemics. J Infect Public Health. 2021;14(1):53-60.
Infection prevention and control initiatives work to prevent the spread of infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria, reduce the need for antibiotics and help curb the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
Infection control practices, from simple handwashing to global vaccination and the use of effective infection prevention measures, are key tools to combat AMR. Preventing drug-resistant infections reduces the use of antibiotics and improves patient outcomes.
SOURCES OF INFECTION
Healthcare settings are high-risk environments for the spread of organisms that cause infections. 7% to 10% of hospitalized patients and 33% of patients in intensive care units contract at least one healthcare-associated infection.1,2
Only 40% of healthcare workers adhere to recommended handwashing practices, although self-reported rates are nearly 100%.3
Medical devices and surgical procedures are potential sources of infection.17% of central-line, 14% of surgical-site and 10% of catheter-associated infections are caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.4
Patients can be a source of transmission of infectious bacteria to caregivers, to other patients and often, to themselves. Up to 30% of individuals carry Staphylococcus aureus, a potentially harmful bacterium.5
Partnering on prevention
At BD, we are leveraging our expertise in diagnostics, vascular access, surgical preparation and critical care to support hospitals’ infection prevention and control programs. BD is committed to helping clinicians improve patient outcomes through the standardization of care and adherence to best practices.
SHEA: In support of the infection prevention efforts of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), BD provides an educational grant for the “Prevention Course in HAI Knowledge and Control”—a free educational resource to keep frontline providers, their families, and patients safe.
International Collaboration: BD has worked with national governments in multiple countries, including the United States, China, Kenya, Cambodia, and India, via public-private partnerships to improve hospitals’ capabilities with infection prevention and control.
Educational Publication Partnerships: BD leverages expertise from internal clinical pharmacists, infectious disease physicians and industry-leading data scientists to produce more than 500 unique analytic tool sets, resulting in publications informing infection prevention guidelines.
Working together to improve processes: BD partners with clinicians in addressing vascular access-related complications by identifying gaps in their current vascular access process.
BD Product Solutions
Systematic infection prevention and control procedures reduce the frequency and extent of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) and the spread of antimicrobial-resistant organisms. Comprehensive product and service offerings from BD help clinicians improve patient outcomes through the standardization of care and adherence to best practices.
-

Vascular access management is vital to help reduce complications and infections, and to improve patient outcomes.
-

Preoperative skin preparation is an important step in helping to limit surgical wound contamination and prevent infection.
-

Products and kits designed to reduce variability or improve compliance in critical care practice.
We must take action against drug-resistant infections, TOGETHER!
References
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial resistance fact sheet. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs194/en/. Accessed November 28, 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About antimicrobial resistance. https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about.html. Accessed May 12, 2017.
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. The latest estimates of global anti-microbial resistance show urgent policy action is needed to save lives. https://www.healthdata.org/news-release/latest-estimates-global-anti-microbial-resistance-show-urgent-policyactionneededsave#:~:text=An%20estimated%204.95%20million%20people,young%20children%20are%20particularly%20affected. Accessed February 8, 2022.
- World Health Organization. Ten threats to global health in 2019. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/ten-threats-toglobal-health-in-2019. Accessed February 8, 2022.
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet.2022;399(10325):629-655.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. More people in the United States dying from antibiotic-resistant infections than previously estimated. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2019/p1113-antibiotic-resistant.html; Accessed June 23, 2022.
- O’Neill J. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20%20Tackling%20a%20crisis%20for%20the%20health%20and%20wealth%20of%20nations_1.pdf. Accessed February 8, 2022.
- Smith R, Coast J. The true cost of antimicrobial resistance. BMJ. 2013;346:f1493.
- World Bank. By 2050, drug-resistant infections could cause global economic damage on par with 2008 financial crisis, http://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2016/09/18. Accessed October 12, 2017.
- Shapiro DJ, Hicks LA, Pavia AT, Hersh AL. Antibiotic prescribing for adults in ambulatory care in the USA, 2007–09. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;69(1):234-240.
- Ukuhor H. The interrelationships between antimicrobial resistance, COVID-19, past, and future pandemics. J Infect Public Health. 2021;14(1):53-60.
What is Stewardship?
Essentially, antibiotic stewardship means being smarter—more discriminating and more appropriate—about how we (as a society) use them.
Antimicrobial stewardship programs in healthcare settings are designed to optimize antibiotic therapies, with the intention of slowing the emergence of drug-resistance.
Accurate and rapid diagnostic testing is a crucial element of stewardship. Diagnostic testing can identify the infection-causing organism, determine whether it is resistant and guide the appropriate therapeutic choice.
BD is committed to three key areas in support of global antibiotic stewardship:
- Delivering updated and new diagnostic tools
- Deploying software to move data from lab to the patient
- Partnering in the development of training tools to foster stewardship
BD partnerships
Globally: BD is working with The Fleming Fund to strengthen laboratories in 19 developing and emerging countries.
BD partnered with the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), a Geneva-based non-governmental organization, to develop the new AMR scorecard for lab quality improvement. A successful rollout of equipment, reagents and training has improved lab capabilities across these countries.
UK: BD partnered with a UK pharmacy chain to demonstrate the effective use of point-of-care tests that diagnose patients with viral infections, resulting in the reduction of the number of unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions.
India: BD partnered with the Ministry of Health in Kerala to increase access to automated blood culture and identification and antibiotic susceptibility technologies at a secondary public sector hospital, to reduce mortality rates due to sepsis.
Diagnostic tests classify infections and guide therapies, enabling clinicians to implement effective antimicrobial interventions
-

Improve sample quality and protect specimen integrity by properly acquiring and managing samples for testing.
-

Reduce the risk of HAIs by efficiently identifying patients colonized with resistant organisms.
-

Guide therapy and prevent unnecessary antimicrobial use by identifying the cause of infection.
-
Optimize the patient treatment plan by determining the specific antimicrobials that inhibit or kill particular bacteria.
Comprehensive Surveillance is critical for public health to identify and respond to emerging threats around the world.
Why is it important?
Surveillance is needed to understand the scope and risk of drug-resistant infections and to catch emerging threats when and where they arise—and develop an appropriate and effective response.
Providing early warnings of outbreaks is a vital part of mitigating AMR. Without surveillance, we will not be able to bring attention and needed resources to address AMR.
BD has contributed extensive data and analytics to evaluate and report the burden of AMR to a range of global organizations, including the:
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IMHE)
- The Center for Disease Dynamics, Economics and Policy (CDDEP)
The BD Health and Economic Outcomes Research (HEOR) team developed an AMR Burden of Disease Tool that illustrates current and anticipated future clinical and economic impacts of AMR across various system levels. BD is helping health systems and facilities in Canada, Southeast Asia, China and elsewhere use this tool.
The BD HealthSight™ platform transforms over 2.3 billion patient messages per year into meaningful analytics and insights for clients, BD business units and the scientific community/industry. We collaborate with other life science companies to publish these critical data sets.
Surveillance includes Reporting, Analysis and Collaboration.
BD partners with organizations around the work to strengthen laboratory diagnostic and reporting systems as well as to train healthcare workers on best practices to improve stewardship and surveillance.
AMR is a global problem and requires a global solution.
A connected medication management system comprising technologies, analytics and surveillance tools can help ensure that medications are available and used appropriately.
-

Empower health systems to identify and report infections, translate data into a tool for HAI management and detect possible outbreaks and clusters of resistant organisms and other important pathogens.
-

Enhances efforts through on-demand, standardized evaluation and reporting of antimicrobial use and resistance.
-

Supports patient care by providing facilities with visibility to their medications through a central view of inventory, orders and usage across the health system.
Raising awareness is crucial because AMR threatens everyone!
Antimicrobial resistance is increasing rapidly worldwide.
Without action, common medical procedures - including surgery, childbirth and chemotherapy - will become increasingly life-threatening.
AMR threatens everyone on Earth.
So all of us need to be resistance fighters…..right here, right now.
As founding sponsor of the Antimicrobial Resistance Fighter Coalition (ARFC), BD supports education, training and partnerships across the globe to raise awareness of AMR and to change behaviors that will help maintain the effectiveness of antibiotics for our future generations.
Who Is ARFC?
The Antimicrobial Resistance Fighter Coalition is a bold collective of like-minded organizations, leaders and individuals united in their commitment to address the threat and burden of antimicrobial resistance.
Training is equally crucial to strengthen microbiology labs globally.
BD and The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, together with a global advisory group of experts, partnered to create the Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) that educate participants about how diagnostics can be leveraged to reduce AMR risks. Lessons learned from COVID-19 are included in the training.
Halting and reversing this massive challenge will require the combined resources and efforts of both public and private sectors. AMR has no single solution, and the challenges cannot be solved without multiple players working collectively on a common AMR agenda. BD will continue to collaborate with global leaders around the world to address this urgent global health concern.
US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)