- Overview
- Safety Innovations
- Economic Value
- Related Products
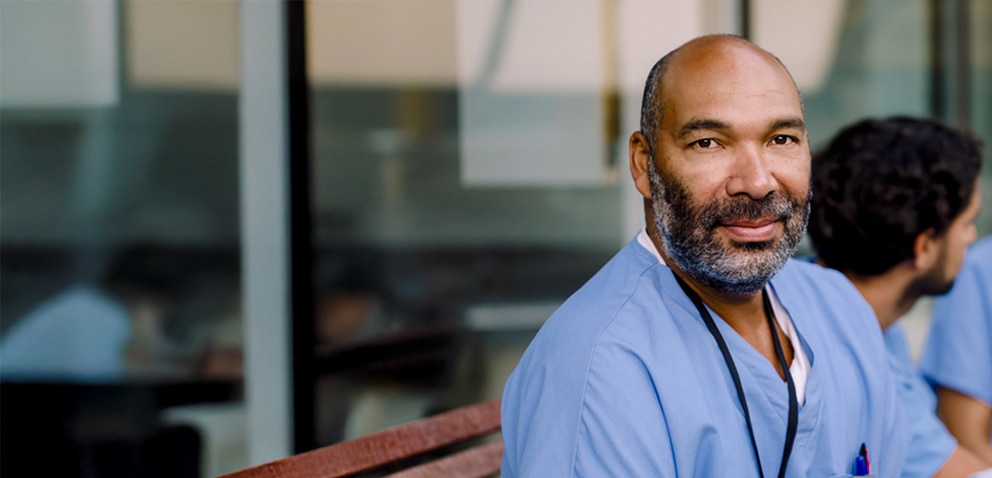
At BD, we see the person beyond the procedure being performed—the healthcare worker dedicated to showing up every day and delivering the highest quality patient care at every stage.
You are why we continue to build on our 125-year legacy of investing in innovation, education and advocacy. Why we place safety at the heart of every innovation, and continually ask how each advancement could protect more and better. Why we work to reduce the steps and complexities of staying safe, so you can focus on your patients. You are why we offer a broad array of healthcare worker safety technologies, spanning the continuum of care from preparation to administration to disposal.
At BD, your safety is our commitment. You are why we do it.
-
Globally-trusted expertise
delivered through holistic safety and training programs
-
$1 billion+ investments
in innovation, education and advocacy
-
Comprehensive portfolio
of healthcare worker safety devices available
-
Clinically-proven outcomes
supported by decades of product use
-
Proven value
through healthcare worker injury-associated cost reduction
-
125-year commitment
to healthcare leadership
Our commitment to your safety doesn’t stop with our devices.
In our effort to advance the world of health and healthcare worker safety, BD published a Global Public Policy Position and actively supports the following objectives that are aligned with best practices to reduce the risk of needlestick injuries and blood exposure for healthcare workers: At BD, your safety is our commitment. You are why we do it.
- Educate stakeholders on the risks of blood exposure and needlestick injury
- Implement reporting and surveillance procedures to monitor the prevalence of needlestick injury and blood exposure in all healthcare facilities
- Mandate safer working practices for all healthcare workers
- Accelerate the adoption of safety-engineered devices
Read our full Global Public Policy Position on Preventing Needlestick Injuries and Blood Exposure Incidents here
The cost of switching to safety-engineered devices (SEDs) from conventional devices isn’t simply a comparison of prices.
From needlestick injuries and blood exposure to hazardous drug exposure, every incident carries potential clinical and emotional burdens for healthcare workers and economic burden for healthcare systems.
Taking steps to increase control of exposures can lead to better clinical, emotional and economic outcomes.
Broad portfolio of healthcare worker safety technologies
BD has long been at the forefront of healthcare worker safety—through far reaching innovation, unparalleled investments and a broad array of healthcare worker safety technologies, spanning the care continuum from preparation to administration and beyond.
BD is a global leader in healthcare worker safety technology, engineering every device to the highest quality and safety standards—so clinicians can confidently focus on their jobs and patients.
The BD portfolio of healthcare worker safety technologies addresses three core safety concerns.
-
Needlestick injuries
-
Blood exposure
-
Hazardous drug exposure
BD understands the value and impact of education and training on healthcare worker safety.
That’s why we invest heavily in training and education initiatives to support healthcare workers in the adoption of new technologies, best practice training in safety and everyday clinical applications, understanding the benefits of safety-engineered devices and more.
Learn more about how we deliver on our commitment to safety in our comprehensive portfolio of products.
Every day, healthcare workers risk their health to deliver the care patients need most.
Just one of these exposures could change everything for a healthcare worker.
-
Any time there is a needlestick injury, there is a risk of exposure to more than 30 dangerous bloodborne pathogens, including HIV, hepatitis B and hepatitis C.5
-
The fear of seroconversion can be an intense emotional burden,6 and healthcare workers experience significant anxiety after occupational exposure to potentially contaminated body fluids.7
-
Handling hazardous drugs puts healthcare workers at risk of short- and long-term health issues such as headaches, hair loss, nausea, organ damage, reproductive problems,8 developmental impairment, genetic issues and even cancer.9
Blood exposure and needlestick injuries can also have a meaningful impact on healthcare system economics.
The use of safety-engineered devices (SEDs) has been proven to prevent needlestick injuries, blood exposure and hazardous drug exposure.
-
when safety devices were used. Education and training were key factors13
-
demonstrated by catheters with blood control technology14
-
The percentage of venipuncture/injection administration injuries that could have “probably” or “definitely” been prevented by safety devices15
-
In surface contamination with the use of a closed system transfer device (CSTD) when preparing cyclophosphamide, ifosamide and 5-fluorouracil (95%, 90% and 65%, respectively)16†
†Compared to standard techniques/ devices for drug preparation and reconstitution
The use of safety-engineered devices (SEDs) has been proven to prevent needlestick injuries, blood exposure and hazardous drug exposure.
-

when safety devices were used. Education and training were key factors13
-

demonstrated by catheters with blood control technology14
-
The percentage of venipuncture/injection administration injuries that could have “probably” or “definitely” been prevented by safety devices15
-
In surface contamination with the use of a closed system transfer device (CSTD) when preparing cyclophosphamide, ifosamide and 5-fluorouracil (95%, 90% and 65%, respectively)16†
†Compared to standard techniques/ devices for drug preparation and reconstitution
Providing clinical, economic and emotional benefits with both short- and long-term implications.
-
Clinical benefit
Short-term implications
Reduction in the risk of needlestick injuries,17 blood exposure14,18 and surface contamination16
Long-term implications
Reduction in risk of transmission of bloodborne pathogens, including HIV and hepatitis19
-
Economic benefit
Short-term implications
Reduction in post-exposure direct and indirect medical costs20
Long-term implicationsAvoidance of long-term treatment costs and costs of litigation20
-
Emotional benefit
Short-term implications
Reduced stress and less anxiety/time off post-needlestick injury21
Long-term implicationsReduction in humanistic burden consequences of needlestick injuries22
Through our broad portfolio of safety-engineered devices, BD is committed to helping clinicians and institutions meet clinical needs and transform safety at each step of the care continuum.
Safety conversion support and management
Risk assessment is a vital first step towards building safer environments and practices. BD offers tools and support to help identify potential harm, assess risk and develop recommendations for change.
Education and training
Our clinical consultants work with clinical leadership to implement training and education programs aligned to industry standards, helping advance clinical skills and knowledge.
Evidence-based budget impact modeling
Our evidence-based budget impact model is specifically designed to help you identify the potential economic impact of safety conversion. Modeling includes the estimated annual economic impact of switching from conventional to SEDs and potential cost savings of avoiding exposures and needlestick injuries.
Single vendor standardization
Standardizing to a single vendor can reduce contract management time, costs, and create efficiencies with product ordering (lower shipping fees) and product management (reduced waste and stock-outs).22,23
Supply continuity and integrated manufacturing
By investing in global capacity and increasing production, we’re taking action on our commitment to improving supply continuity for critical-to-healthcare products. We employ vertical integration for full control and multi-step inspection to ensure optimal quality in manufacturing our devices.
Learn more about how we deliver on our commitment to safety in our comprehensive portfolio of products.
- Jagger J, Perry J, Parker G, Phillips EK. Nursing2011 survey results: Blood exposure risk during peripheral I.V. catheter insertion and removal. Nursing. 2011;41(12):45-49. doi:10.1097/01.NURSE.0000407678.81635.62
- d’Ettorre G. Needlestick and Sharp Injuries Among Registered Nurses: A Case-Control Study. Ann Work Expo Health. 2017;61(5):596-599.
- Glenngard AH, Persson U. Costs associated with sharps injuries in the Swedish healthcare setting and potential cost savings from needle-stick prevention devices with needle and syringe. Scand J Infect Dis. 2009;41(4):296-302.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Hazardous drug exposures in health care. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Web site. http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/hazdrug. Accessed May 16, 2022.
- European Biosafety Network. Prevention of Sharps Injuries in the Hospital and Healthcare Sector. European Biosafety Network Implementation Guidance Toolkit for EU Council Directive 2010/32/EU. January 2013 Available at: www.europeansafetynetwork.eu. Accessed May 16, 2022.
- Hambridge K, Nichols A, Endacott R. The impact of sharps injuries on student nurses: a systematic review. Br J Nurs. 2016;25(19):1064-1071. doi:10.12968/bjon.2016.25.19.1064
- Meienberg F, Bucher HC, Sponagel L, Zinkernagel C, Gyr N, Battegay M. Anxiety in health care workers after exposure to potentially HIV-contaminated blood or body fluids. Swiss Med Wkly. 2002;132(23-24):321-324.
- Connor TH, Lawson CC, Polovich M, McDiarmid MA. Reproductive health risks associated with occupational exposures to antineoplastic drugs in health care settings: a review of the evidence. J Occup Environ Med. 2014;56(9):901-910.
- Hansen J, Olsen JH. Cancer morbidity among Danish female pharmacy technicians. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1994;20(1):22-26.
- O’Malley EM, Scott RD2nd, Gayle J, et al. Costs of management of occupational exposures to blood and body fluids. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007;28(7):774-782.
- Richardson D, Kaufman L. Reducing blood exposure risks and costs associated with SPIVC insertion. Nurs Manage. 2011;42(12):31-34.
- Frickman H, Schmeja W, Reisinger E, et al. Risk reduction of needle stick injuries due to continuous shift from unsafe to safe instruments at a German university hospital. Eur J Microbial Immunol (Bp). 2016 Sep 29;6(3):227-37.
- De Carli G et al. The importance of implementing safe sharps practices in the laboratory setting in Europe. Biochem Med 2014;24(1):45–56.
- Onia R, Eshun-Wilson I, Arce C, Ellis C, Parvu V, Hassman D, Kassler-Taub K. Evaluation of a new safety peripheral IV catheter designed to reduce mucocutaneous blood exposure. Curr Med Res Opin. 2011;27(7):1339-1346.
- Cullen BL et al. Potential for reported needlestick injury prevention among healthcare workers through safety device usage and improvement of guideline adherence: expert panel assessment. J Hosp Infect 2006;63:445–451.
- Sessink PJ, Connor TH, Jorgenson JA, Tyler TG. Reduction in surface contamination with antineoplastic drugs in 22 hospital pharmacies in the US following implementation of a closed-system drug transfer device. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2011;17(1):39-48. doi:10.1177/1078155210361431
- Elseviers MM, Arias-Guillen M, Gorke A, Arens HJ. Sharps injuries amongst healthcare workers: review of incidence, transmissions and costs. J Ren Care 2014;40:150e156.
- Bausone-Gazda D, Lefaiver CA, Walters SA. A randomized controlled trial to compare the complications of 2 peripheral intravenous catheter-stabilization systems. J Infus Nurs. 2010;33(6):371-384.
- Montella E, Shiavone D, Apicella L, Di Silverio P, Gaudiosi M, Ambrosone E, et al. Cost-benefit evaluation of a preventive intervention on the biological risk in health: the accidental puncture during the administration of insulin in the University Hospital “Federico II” of Naples. Ann Ig. 2014 May-Jun:26(3):272-8.
- Mannocci A, De Carli G, Di Bari V, Saulle R, Unim B, Nicolotti N, et al. How much do needlestick injuries cost? A systematic review of the economic evaluations of needlestick and sharps injuries among healthcare personnel. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2016 Jun;37(6)635-46.
- Green B, Griffiths EC. Psychiatric consequences of needlestick injury. Occup Med (Lond). 2013 Apr;63(3):183-8.
- d’Ettorre G. Job stress and needlestick injuries: which targets for organizational interventions? Occup Med (Lond). 2016 Jul 31.
- Mullins D, Persaud EJ, Ferko NC, Knight B, Tripodi D, Delatore P. SKU optimization initiatives can create cost savings in an era of value-based care. Healthcare Financial Management Association. 2019.
Related Products
-
-
The BD PhaSeal™ system is airtight and leakproof to protect your staff from hazardous drug exposure during drug preparation, administration and disposal.
-
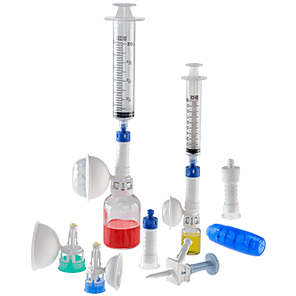
Safety. Performance. Ergonomics. Ease of use. We’ve advanced them all in the BD PhaSeal™ Optima CSTD.
-
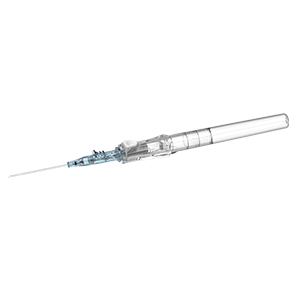
Confidently keep blood in its place—away from you and your patients.
-
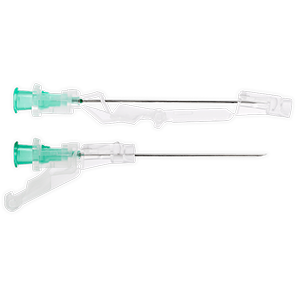
BD SafetyGlide™ Needles have Activation Assist™ Technology, making a safe injection easier and more efficient.
-

The BD® HD Check system reliably* detects surface contamination on multiple surfaces.


