BD supports you in implementing antimicrobial stewardship programmes overview.
Infection prevention
BD supports you in enhancing compliance to guidelines and offers you safe alternatives to help reduce SSIs, CAUTIs and CRBSIs with a portfolio of solutions which include innovative technologies and services.
Sample quality
BD supports you in improving sample quality by optimising processes and standardising practices with a portfolio of solutions which include innovative technologies and services.
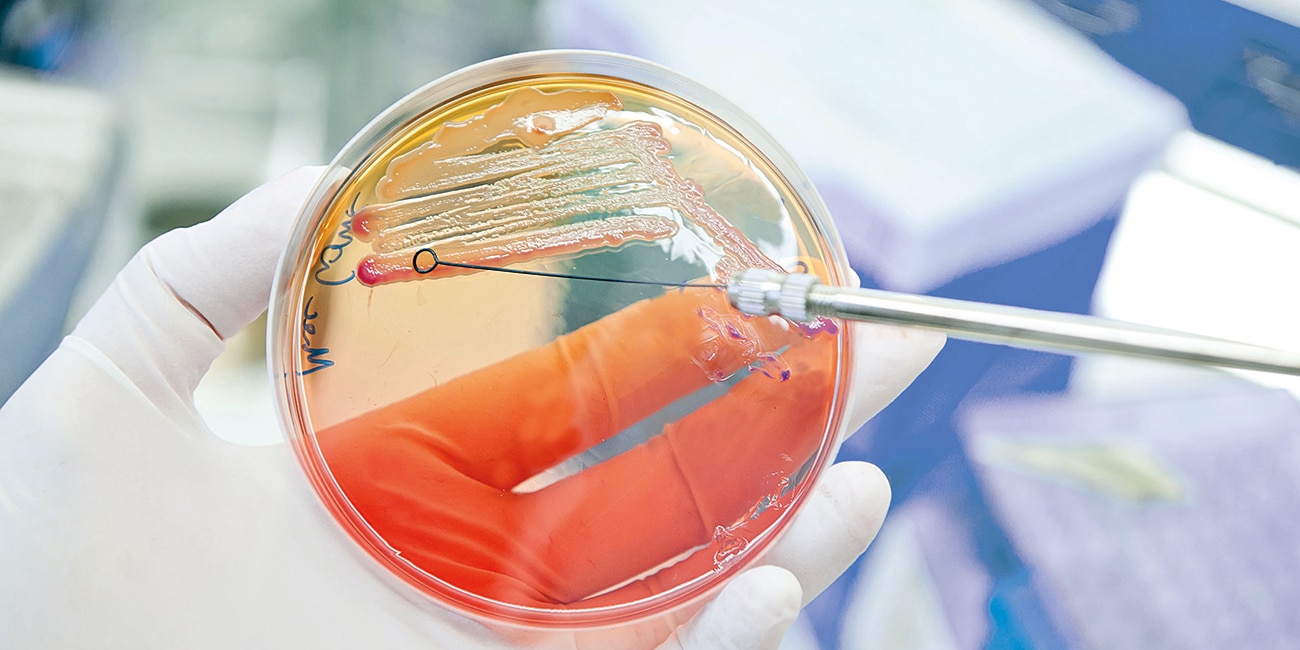
Diagnostic accuracy and timeliness
BD supports more rapid, accurate and appropriate diagnostic identification enabling effective clinical decision-making that aid in mitigating antimicrobial resistance with a portfolio of solutions which include innovative technologies and services.
Surveillance and reporting
BD supports you in enabling remote multi-site diagnostic result availability with digital infrastructure for faster decision-making with a porfolio of solutions which include innovative technologies and services.
BD supports change management and continuous quality improvement.