Steripath® Initial Specimen Diversion Device®
Achieve sustained near-zero blood culture contamination rates 1-6
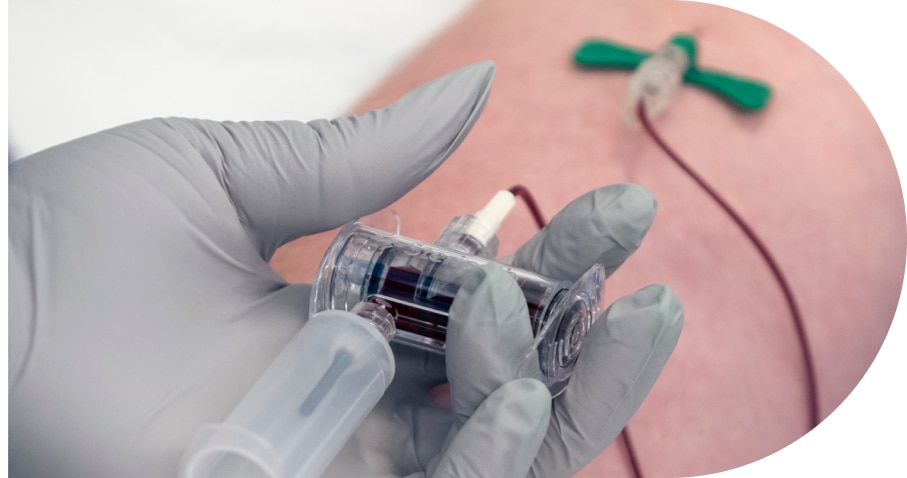

Integrate the Steripath® Initial Specimen Diversion Device® (ISDD®)in your blood culture protocol to achieve near-zero blood culture contamination rates.1-6

Despite best efforts, hospitals still face specimen contamination issues
Even when following best practice procedures for skin preparation, contamination can still occur since up to 20% of the skin flora remains viable in the keratin layer of the skin.7
False positive results due to contamination and insufficient blood culture volume can carry numerous downstream consequences, such as misdiagnosis, unnecessary broad spectrum antibiotic treatment, delayed antibiotic de-escalation, prolonged time to accurate diagnosis, repeat diagnostic testing, increased length of stay, unnecessary costs, and added strain to health careinfrastructure.8-10

A simple, all-in-one evidence-based solution
Steripath® ISDD® is an FDA 510(k)-cleared device specifically indicated to reduce blood culture contamination. It is backed by 9 studies, supporting sustained results of zero or near-zero blood culture contamination rates for both peripheral stick and fresh peripheral IV start blood culture draws.1-6,11-13
By obtaining blood culture specimens free from contaminants, you can ensure that a positive is a true positive and be confident that the right antibiotic treatment decisions can be made as early as possible.

A safe and streamlined workflow
Steripath® ISDD® utilizes the BD Vacutainer® Push Button Blood Collection Set technology which enables single-handed, in vein activation that retracts the needle and can reduce accidental needlestick injuries by 88% as compared to manual safety wingsets.14,15
In addition, Steripath® ISDD® seamlessly integrates with BD BACTEC™ blood culture media and BD Vacutainer® blood collection tubes for streamlined and efficient blood collection.
Create the opportunity to remove avoidable errors, variability and inefficiencies in blood culture collection.
By reducing false-positive blood cultures, Steripath® can help you achieve sustainable clinical and economical impact.
-
Hospital costs
Decrease annual hospital costs by an average of $1.9M for small to medium-sized U.S. hospitals.13
-
Patient outcomes
Shorten average length of stay by 2.2 days.12,13
-
Antimicrobial stewardship
Achieve up to a 31% incremental reduction in vancomycin days of therapy.4

Bloodstream Infection Solution

Magnolia Medical Technologies
